Atmosphere Browser User Guide
Introduction
On SpectralCalc.com, we use the term atmosphere to mean a set of vertical profiles of one or more species.A vertical profile gives the volume-mixing ratio (vmr) of a species (or the temperature) as a function of altitude. An atmosphere must have a single temperature profile, and can contain any number of vmr profiles. SpectralCalc has six system-supplied atmospheres for Earth, and one for Mars. Each system-supplied atmosphere contains a temperature profile and vmr profiles for the common species in that planet's atmosphere. Using the Atmosphere Browser, you can view the vertical profiles from any atmosphere, or create/ modify your own custom atmosphere.
Examining the contents of an atmosphere
To view the contents of an atmosphere, select a single atmosphere from the list and click the Plot/Extract
Species button:![]() You can choose to plot/extract either 1) the vertical profile of a single species, or 2) all vmrs at a single altitude.
You can choose to plot/extract either 1) the vertical profile of a single species, or 2) all vmrs at a single altitude.
Once you have made your selections, pressing Plot Species will produce a graph of the data. Subsequent graphs will 'push down' any earlier graphs on the page. To retrieve the raw data as text, you can click the Text file link beneath any plot. (Right-click to save the data to a local file on your computer).
Alternatively, to view or download the raw data as text without plotting it, press the Extract Data button. This will produce a link to a file containing the data in plain text format. Clicking the link will open a new window with the data. Right-clicking on the link will allow you to easily download the file to your computer.
Creating a custom atmosphere
To create your own custom atmosphere, use the Atmosphere Browser tool and click the Create Atmosphere button:![]() . You will be prompted for a name, planet, latitude and description. The planet and latitude will be used to determine the atmosphere's radius of curvature and gravity in any simulations using this atmosphere.
. You will be prompted for a name, planet, latitude and description. The planet and latitude will be used to determine the atmosphere's radius of curvature and gravity in any simulations using this atmosphere.
Often it is most convenient to begin by duplicating an existing atmosphere, then modifying some of the profiles.This prevents the lengthier task of uploading vertical profiles for each species.
Duplicating an atmosphere
Creating a custom atmosphere 'from scratch' can be somewhat time
consuming if many species will be needed. In these cases, it is generally more efficient just to duplicate an
existing atmosphere and then modify one or more of the species of interest. To duplicate an atmosphere, simply select an atmosphere to copy, and click the Duplicate Atmosphere icon:![]() . You will be prompted to name the new atmosphere and specify
the latitude and add an optional description. (The latitude is used in simulations, for example, to
account for the slight oblateness of the planet.)
. You will be prompted to name the new atmosphere and specify
the latitude and add an optional description. (The latitude is used in simulations, for example, to
account for the slight oblateness of the planet.)
Adding or replacing a vertical profile
To add or replace a vertical profile in a custom atmosphere,
select the atmosphere and click the Add/Replace
Species button: ![]() Choose the species from the dropdown
menu, and the name of the file to upload. (If you select temperature, you will also be asked for
a surface pressure. SpectralCalc will build up the rest of the pressure profile hydrostatically from the surface.)
If the atmosphere already has a profile for this species, you will be alerted before overwriting this
profile. Once initiated, the file will be uploaded to our server, validated, and inserted into the atmosphere. Details on the required file format and contents are below.
Choose the species from the dropdown
menu, and the name of the file to upload. (If you select temperature, you will also be asked for
a surface pressure. SpectralCalc will build up the rest of the pressure profile hydrostatically from the surface.)
If the atmosphere already has a profile for this species, you will be alerted before overwriting this
profile. Once initiated, the file will be uploaded to our server, validated, and inserted into the atmosphere. Details on the required file format and contents are below.
Deleting a vertical profile from an atmosphere
To delete a vertical profile from a custom atmosphere,
select the atmosphere and click the Delete Species button: ![]() . Identify the species (or set of species) that you wish to delete by checking the appropriate entries in the Species dropdown menu. When you are done selecting, press Delete.
. Identify the species (or set of species) that you wish to delete by checking the appropriate entries in the Species dropdown menu. When you are done selecting, press Delete.
Modifying an atmosphere
You can modify an atmosphere's name, planet, latitude and
description at any time by clicking the Modify Atmosphere button: ![]() . Enter the desired modifications and click Save Changes when complete.
. Enter the desired modifications and click Save Changes when complete.
File requirements for uploading vertical profiles
The data must be in a two-column text file. The first column is the volume mixing ratio (vmr) or temperature in Kelvin, and the second is the altitude in km. The columns can be space, comma or tab delimited. Any line beginning with a # character will be ignored as a comment line. Any text to the right of the second column will also be ignored.
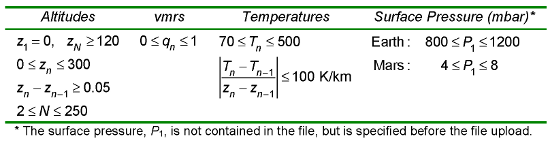
Altitudes are assumed to be in km, and must extend from the ground (0 km) to at least 120 km, with at least 2 but no more than 250 points. Layers can be variable thickness, but no layer can be thinner than 0.05 km.
Volume Mixing Ratios (vmrs) must be between 0 and 1 (inclusive).
Temperatures must be between 70 and 500 K (inclusive), and no individual layer's lapse rate can exceed ±100K/km.
The following table summarizes these acceptable ranges and constraints. zn, qn and Tn are the altitude, vmr and temperature of layer n, and N is the total number of layers.
Glossary
Atmosphere: An atmosphere contains profiles of temperature and gas concentrations at altitudes spanning 0 to 120 km. Each atmosphere has an associated planet and latitude (used to determine radius and gravity in simulations). There are six system-supplied atmospheres for Earth, and one for Mars. Custom atmospheres can be created and populated with user-supplied vertical profiles. If you choose a custom atmosphere as the primary atmosphere in a simulation, then the secondary, system-supplied atmosphere will be used for any species that may be needed but are missing in your custom atmosphere.
Vertical Profile: an array of volume mixing ratios (vmrs) or temperatures (in K) and the corresponding altitudes (in km). Vertical profiles are increasing in altitude and span 0 to at least 120 km. During a simulation, a vertical profile will be resampled to the altitudes needed by that particular scenario.